

68008 Assembly programming for the Sinclair QL
| Specs: The 68008 is a cut down 68000 - it's address bus and data bus are smaller (normal spec of 68k in brackets)
|
|
ChibiAkumas Tutorials
| Lesson P4 - Bitmap Functions on the Sinclair QL | |
| Lesson P10 - Cursor reading on the Sinclair QL | |
| Lesson P22 - Sound on the Sinclair QL | |
Documentation
Sinclair QL Software Developer's Guide - Covers all the traps and the best detail of the hardware.
QL Manual (Introduction,Beginners,Concepts,Keywords) - basics of using the ql
Assembly Language on the Sinclair QL - decent beginners programming book
RGB Cable for Sinclair QL - Make a RGB or SCART cable for the QL
Microdrive Repair - Service your microdrive!
VDrive QL - MDV Emulator
Memory Map
Note: the exact address of the sysem elements marked * may vary depending on firmware and ram installed - these examples only based on a 128k system...
Also note: Screen 2 shares the same ram as the system - we can turn off the system with the commands:
Trap #0
ori #0700,sr
But this will render many of the other traps unusable
| Address | Purpose | Details |
| $00000 | Onboard
48k Rom |
|
| $0C000 | 16K
Rom Cartridge |
|
| $10000 | Onboard I/O | |
| $18000 | (R) RTC byte 0 / (W) RTC Reset | |
| $18001 | (R) RTC byte 1 / (W) RTC Step | |
| $18002 | (R) RTC byte 2 / (W) Transmit control | |
| $18003 | (R) RTC byte 3 / (W) IPC link control | |
| $18020 | (R) Microdrive/RS232c status / (W) Microdrive control | |
| $18021 | (R) Interrupt/IPC status / (W) Interrupt control | |
| $18022 | (R) Microdrive Track 1 / (W) Microdrive / RS232C data | |
| $18023 | (R) Microdrive Track 2 / (W) Display control | |
| $18063 | Screen Mode S---C-O- On Colordepth Screenpage | |
| $20000 | Screen 1 | Screen Ram |
| $28000 | Screen 2 / System |
system (systemvars*) |
| $2847C | System stack pointer* | |
| $28E00 | Base of Common Heap* | |
| $2BC00 | Free area* | |
| $30000 | Running Programs |
Free area |
| $37200 | Basic area* | |
| $38000 | User Stack pointer* | |
| $38000 | Prog data* | |
| $40000 | Add
on ram (up to 512k) |
|
| $C0000 | Add
on peripherals |
|
| $E0000 | Add
on Rom (up to 128k) |
|
| $FFFFF | End of address space |
Traps!
| Traps 0-4 have special purposes for
system events... We can control the screen without traps, but keyboard and sound can only be done with them! A summary of the traps is shown below, see Sinclair QL Software Developer's Guide for full details |
|
| Trap | D0 | Name | Description |
| #1 | $15 | MT.ACLCK | Adjust the clock |
| #1 | $0A | MT.ACTIV | Activate a job |
| #1 | $16 | MT.ALBAS | Allocate BASIC program area |
| #1 | $18 | MT.ALCHP | Allocate common heap area |
| #1 | $0C | MT.ALLOC | Allocate an area in a heap |
| #1 | $0E | MT.ALRES | Allocate resident procedure area |
| #1 | $12 | MT.BAUD | Set the baud rate |
| #1 | $01 | MT.CJOB | Create a job in transient program area |
| #1 | $10 | MT.DMODE | Set or read the display mode |
| #1 | $06 | MT.FREE | Find largest contiguous free space that may be allocated in the transient program area |
| #1 | $05 | MT.FRJOB | Force remove job from transient program area |
| #1 | $00 | MT.lNF | System information |
| #1 | $11 | MT.lPCOM | Send a command to the IPC (sound/keyboard) |
| #1 | $02 | MTJINF | Information on a job |
| #1 | $0D | MT.LNKFR | Link a free space (back) into a heap |
| #1 | $1A | MT.LXINT | Link an external interrupt service routine |
| #1 | $1C | MT.LPOLL | Link a polling 50/60 Hz service routine |
| #1 | $1E | MT.LSCHD | Link a scheduler loop task |
| #1 | $20 | MT.LlOD | Link an I/O device driver |
| #1 | $22 | MT.LDD | Link or a directory device driver into the operating system |
| #1 | $0B | MT.PRIOR | Change job priority |
| #1 | $13 | MT.RCLCK | Read the clock |
| #1 | $17 | MT.REBAS | Release BASIC program area |
| #1 | $19 | MT.RECHP | Release common heap area |
| #1 | $09 | MT.RELJB | Release a job |
| #1 | $0F | MT.RERES | Release resident procedure area |
| #1 | $04 | MT.RJOB | Remove job from transient program area |
| #1 | $1B | MT.RXINT | Remove an external interrupt service routine a |
| #1 | $1D | MT.RPOLL | Remove a polling 50/60 Hz service routine |
| #1 | $1F | MT.RSCHD | Remove a scheduler loop task |
| #1 | $21 | MT.RIOD | Remove an IO device driver |
| #1 | $23 | MT.RDD | Remove a directory device driver from the operating system |
| #1 | $14 | MT.SCLCK | Set the clock |
| #1 | $08 | MT.SUSJB | Suspend a job |
| #1 | $07 | MT.TRAPV | Set the per-job pointer to trap vectors |
| #2 | $02 | IO.CLOSE | Close a channel |
| #2 | $04 | IO.DELET | Delete a file |
| #2 | $03 | IO.FORMT | Format a sectored medium |
| #2 | $01 | IO.OPEN | Open a channel |
| #3 | $40 | FS.CHECK | Check all pending operations on a file |
| #3 | $41 | FS.FLUSH | Flush buffers for this file |
| #3 | $47 | FS.HEADR | Read file header |
| #3 | $46 | FS.HEADS | Set file header |
| #3 | $48 | FS.LOAD | Load file into memory |
| #3 | $45 | FS.MDINF | Get information about medium |
| #3 | $42 | FS.POSAB | Position file pointer absolute |
| #3 | $43 | FS.POSRE | Position file pointer relative |
| #3 | $49 | FS.SAVE | Save file from memory |
| #3 | $04 | IO.EDLIN | Edit a line of characters (console driver only) |
| #3 | $01 | IO.FBYTE | Fetch a byte |
| #3 | $02 | IO.FLlNE | fetch a line of characters terminated |
| #3 | $03 | IO.FSTRG | fetch a string of bytes |
| #3 | $00 | IO.PEND | Check for pending input |
| #3 | $05 | IO.SBYTE | Send a byte |
| #3 | $07 | IO.SSTRG | Send a string of bytes |
| #3 | $0C | SD.BORDR | Set the border width and colour |
| #3 | $20 | SD.CLEAR | clear all of window |
| #3 | $21 | SD.CLRBT | clear top of window |
| #3 | $22 | SD.CLRLN | clear bottom of window |
| #3 | $23 | SD.CLRRT | clear cursor line |
| #3 | $24 | SD.CLRTP | clear right hand end of cursor line |
| #3 | $0E | SD.CURE | Enable the cursor |
| #3 | $0F | SO.CURS | Suppress the cursor |
| #3 | $09 | SD.EXTOP | Call an extended operation |
| #3 | $2E | SO.FILL | Fill rectangular block in window |
| #3 | $35 | SD.FLOOD | Turn area flood on and off |
| #3 | $25 | SD.FOUNT | Set or reset the fount |
| #3 | $1B | SD.PAN | pan all of window |
| #3 | $1E | SO.PANLN | pan cursor line |
| #3 | $1F | SO.PANRT | pan right hand end of cursor line |
| #3 | $17 | SD.PIXP | Position cursor using pixel coordinates |
| #3 | $30 | SD.POINT | Draw a point |
| #3 | $31 | SD.LINE | Draw a line |
| #3 | $32 | SD.ARC | Draw an arc |
| #3 | $33 | SD.ELlPS | Draw an ellipse |
| #3 | $34 | SD.SCALE | Set scale |
| #3 | $36 | SD.GCUR | Set Graphics cursor pos |
| #3 | $10 | SD.POS | absolute position |
| #3 | $11 | SD.NCOL | tabulate |
| #3 | $12 | SD.NL | newline |
| #3 | $13 | SD.NROW | previous column |
| #3 | $14 | SD.PCOl | next column |
| #3 | $15 | SD.PROW | previous row |
| #3 | $16 | SD.TAB | next row |
| #3 | $0A | SD.PXENQ | enquiry in pixel coordinates |
| #3 | $0B | SD.CHENQ | enquiry in character coordinates |
| #3 | $26 | SD.RECOL | Recolour a window |
| #3 | $18 | SD.SCROL | scroll all of window scroll |
| #3 | $19 | SO.SCRBT | top of window scroll |
| #3 | $1A | SO.SCRTP | bottom of window |
| #3 | $2A | SD.SETFL | set flash |
| #3 | $2B | SD.SETUL | set underscore |
| #3 | $2C | SD.SETMD | Set the character writing or plotting mode |
| #3 | $27 | SO.SETPA | set paper colour |
| #3 | $28 | SO.SETST | set strip colour |
| #3 | $29 | SO.SETIN | set ink colour |
| #3 | $20 | SD.SETST | Set character size and spacing |
| #3 | $0D | SD.WDEF | Redefine a window |
System Vars
| A pointer to the system vars can be returned using the commands
shown to the right... the pointer will be returned in A0 |
move.l #$0,d0 ;Info
(a0=Sysvars) Trap #1 |
| Var | Pos | Length | Meaning |
| SV_IDENT | $00 | word | identification word |
| SV_CHEAP | $04 | long | base of common heap area |
| SV_CHPFR | $08 | long | first free space in common heap area |
| SV_FREE | $0C | long | base of free area |
| SV_BASIC | $10 | long | base of basic area |
| SV_TRNSP | $14 | long | base of transient program area |
| SV_TRNFR | $18 | long | first free space in transient program area |
| SV_RESPR | $1C | long | base of resident procedure area |
| SV_RAMT | $20 | long | top of ram (+1) |
| SV_RAND | $2E | word | random number |
| SV_POLLM | $30 | word | count of poll interupts missed |
| SV_TVMOD | $32 | byte | 0 if not TV display |
| SV_SCRST | $33 | byte | screen status (0= active) |
| SV_MCSTA | $34 | byte | current value of display control register |
| SV_PClNT | $35 | byte | current value of interrupt control/mask register |
| SV_NETNR | $37 | byte | network station number |
| SV_I2LST | $38 | long | pointer to list of interrupt 2 drivers |
| SV_PLlST | $3C | long | pointer to list of polled tasks |
| SV_SHLST | $40 | long | pointer to list of scheduler tasks |
| SV_DRLST | $44 | long | pointer to list of device drivers |
| SV_DDLST | $48 | long | pointer to list of directory device drivers |
| SV_KEYQ | $4C | long | pointer to a keyboard queue |
| SV_TRAPV | $50 | long | pointer to the trap redirection table |
| SV_CAPS | $88 | word | caps lock |
| SV_ARBUF | $8A | word | autorepeat buffer |
| SV_ARDEL | $8C | word | autorepeat delay |
| SV_ARFRQ | $8E | word | autorepeat 1/freq |
| SV_ARCNT | $90 | word | autorepeat count |
| SV_CQCH | $92 | word | keyboard change queue character code |
| SV_SOUND | $96 | word | sound status |
| SV_SER1C | $98 | long | receive channel 1 queue address |
| SV_SER2C | $9C | long | receive channel 2 queue address |
| SV_TMODE | $AO | byte | ZX8302 transmit mode (includes baudrate) |
| SV_CSUB | $A2 | long | subroutine to jump to on CAPSLOCK |
| SV_TIMO | $A6 | word | timeout for switching transmit mode |
| SV_TIMOV | $A8 | word | value of switching timeout (two characters) |
| SV_FSTAT | $AA | word | flashing cursor status |
| SV_BTPNT | $54 | long | pointer to most recent slave block entry |
| SV_BTBAS | $58 | long | pointer to base of slave block table |
| SV_BTTOP | $5C | long | pointer to top of slave block table |
| SV_JBTAG | $60 | word | current value of job tag |
| SV_JBMAX | $62 | word | highest current job number |
| SV_JBPNT | $64 | long | pointer to current job table entry |
| SV_JBBAS | $68 | long | pointer to base of job table |
| SV_JBTOP | $6C | long | pointer to top of job table |
| SV_CHTAG | $70 | word | current value of channel tag |
| SV_CHMAX | $72 | word | highest current channel number |
| SV_CHPNT | $74 | long | pointer to last channel checked |
| SV_CHBAS | $78 | long | pointer to base of channel table |
| SV_CHTOP | $7C | long | pointer to top of channel table |
| SV_MDRUN | $EE | byte | which drive is running? |
| SV_MDCNT | $EF | byte | microdrive run-up run-down counter |
| SV_MDDID | $F0 | 8 bytes | drive ID*4 of each microdrive |
| SV_MDSTA | $F8 | 8 bytes | status 0=no pending ops |
| SV_FSDEF | $100 | 16*long | pointers to file system physical definition |
| SV_FSLST | $140 | long | pointer to list offile channel definitions |
Screen Layout
| The Screen is memory mapped from $20000-$28000, There are two possible screen modes, configured by bit 3 of port $18063 setting a 0 give 4 colors at 512x256 with Black,Red,Green and White setting a 1 give 8 colors at 256x256 with Black, R, G B, C, M, Y and White There is no palette - the colors are fixed. |
4 Color mode:
8 Color mode: (F is flashing)
|
Flashing in 8 color mode
| Flashing only works in 8 color mode -it's a HARDWARE flash, and
does not use th interrupts or firmware. A flashing bit of 1 will toggle flashing ON or OFF... flashing always starts as OFF at the start of a line When a Flashing bit 1 is set - all subsequent pixels will flash between their normal defined color and the color of the pixel with the flashing bit set. |
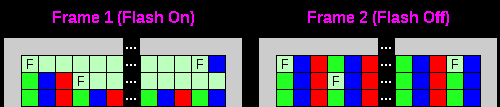 F= Flashing bit of 1
|
Vsync
| If we want to test for Vsync (the start of screen redraw) we need
to use Port $18021... bit 3 will go high (1) when Vsync starts... we
need to write a 1 to that same bit at the same port to clear the
Vsync event... Therefore, in effect we can write 255 to port $18021, then read from $18021 until it's nonzero to get the Vsync event. |
move.b #%11111111,$18021 ;Clear interrupt bits waitVBlankAgain: move.b $18021,d0 ;Read in interrupt state tst.b d0 ;Wait for an interrupt beq waitVBlankAgain |
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
| $18021 Read | B | M | R | X | F | T | I | G | B=Baud
state, M=Microdrive
inactive, R=Rtc
state, X=eXternal
Interrupt, F=Frame
vsync, T=Transmit
interrupt, I=IPC
Interface interrupt G=Gap
interrupt (microdrive) |
| $18021 Write | R | F | M | X | F | T | I | G | R=tRansmit mask, F=interFace mask, M=gap Mask,X=reset eXternal Interrupt,F=reset Frame vsync, T=reset Transmit interrupt, I=reset IPC Interface interrupt G=reset Gap interrupt |
Keyboard Layout
| Reading in from the keyboard has to
be done with Trap 1 - command 9 We have to send a sequence of command bytes - with byte 6 as the row number - the trap will return a byte in D1 - with a bit high when the button is down. An example of the command is shown to the right - this example will read in row 1 The QL can take two external joysticks via the CTL ports (CTL1 and CTL2) - however these actully map to the keyboard Joystick 1 (CTL1) uses Up, Down, Left, Right and Space Joystick 2 (CTL2) uses F4, F2, F1, F3 and F5 |
lea keycommand,a3 move.b #$11,d0 Trap #1 keycommand: dc.b $09 ;0 dc.b $01 ;1 dc.l 0 ;2345 dc.b 1 ;6 - Row dc.b 2 ;7 |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | |
| 7 | Shift | Ctrl | Alt | X | V | / | N | , |
| 6 | 8 | 2 | 6 | Q | E | O | T | U |
| 5 | 9 | W | I | Tab | R | - | Y | |
| 4 | L | 3 | H | 1 | A | P | D | J |
| 3 | I | Caps | K | S | F | = | G | ; |
| 2 | | | Z | . | C | B | pound | M | ~ |
| 1 | Enter | Left / J1-L | Up /
J1-U |
Esc | Right / J1-R | \ | Space / J1-F | Down / J1-D |
| 0 | F4/ J2-U | F1 / J2-L | 5 | F2 / J2-D | F3 / J2-R | F5 / J2-F | 4 | 7 |
Sound Commands
| Sound commands have to be passed via
the Bios, using the same kind of commands as with the keyboard. You need to adjust the Pitch settings to change the sound, and you can change the randomness bits to make the sound distorted, It seems it's not possible to change the volume! |
lea SoundCommand,a3 ; These three lines move.b #$11,d0 ; Stop the note trap #1 SoundCommand: dc.b $A ; Command dc.b 8 ; Bytes to follow dc.l $0000aaaa ; Byte Parameters dc.b 0 ; Pitch 1 dc.b 0 ; Pitch 2 dc.w 0 ; interval between steps (0,0), dc.w $FFFF ; Duration (65535) dc.b 0 ; step in pitch (4bit) / wrap (4bit) dc.b 0 ; randomness of step (4bit) / fuzziness (4bit) dc.b 1 ; No return parameters |
| The sound chip has a special 'silent' command - it's similar to the sound command, but with fewer parameters! |
lea SilentCommand,a3 ; These three lines move.b #$11,d0 ; Stop the note trap #1 SilentCommand: dc.b $B ; Command byte dc.b 0 ;Bytes to follow dc.l $0 ; Send no data dc.b 1 ; No return parameters |
Trap #1 - MT.IPCOM
| Parameter | Byte Offset | Size (bytes) | Bits | Purpose | Example (sound on) |
Example (sound off) |
| 0 | 1 | %----CCCC | Command Byte $0A=Sound on / $0B=Sound off | $A | $B | |
| 1 | 1 | %LLLLLLLL | L=Length of command in bytes | $8 | 0 | |
| 2 | 4 |
%llLLllLLllLLllLL %llLLllLLllLLllLL |
LL/ll=Length of parameters (%01/11=nothing %10=8 bits %00=4 Least significant bits) |
$0000AAAA | 0 | |
| 1 | 6 | 1 |
%HHHHHHHH | Pitch H | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 7 | 1 |
%LLLLLLLL | Pitch L | 0 | |
| 3+4 | 8 | 2 |
%IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII | Interval between steps | 0 | |
| 5+6 | 10 | 2 |
%DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD | Duration | $FFFF | |
| 7 | 12 | 1 |
%SSSSWWWW | Step / Wrap | 0 | |
| 8 | 13 | 1 |
%RRRR/FFFF | Randomness / Fuzziness | 0 | |
| 14 | 1 |
%------LL | L=Reply length (%01/11=nothing %10=8 bits %00=4 Least significant bits) |
1 |
Using the microdrive
You'll need to know a few commands to work with the microdrive
The microdrives are identified my mdv1_ mdv2_ and so on
| See contents of microdrive | DIR mdv1_ |
| copy a file from one microdrive to another | COPY mdv1_ mdv2_ |
| Load a file, show it's contents and run it | LOAD mdv1_bord LIST RUN |
| Load and run | LRUN mdv1_bord |
| Save a file | SAVE mdv1_bord |
| Append another filer | MERGE mdv_prog2 |
| View Options |
| Default Dark |
| Simple (Hide this menu) |
| Print Mode (white background) |
| Top Menu |
| ***Main Menu*** |
| Youtube channel |
| Patreon |
| Introduction to Assembly (Basics for absolute beginners) |
| Amazon Affiliate Link |
| AkuSprite Editor |
| ChibiTracker |
| Dec/Bin/Hex/Oct/Ascii Table |
| Alt Tech |
| Archive.org |
| Bitchute |
| Odysee |
| Rumble |
| DailyMotion |
| Please note: I wlll upload more content to these alt platforms based on the views they bring in |
| 68000 Content |
| ***68000 Tutorial List*** |
| Learn 68000 Assembly |
| Hello World Series |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Simple Samples |
| Grime 68000 |
| 68000 Downloads |
| 68000 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 68000 Platforms |
| Amiga 500 |
| Atari ST |
| Neo Geo |
| Sega Genesis / Mega Drive |
| Sinclair QL |
| X68000 (Sharp x68k) |
| 8086 Content |
| Learn 8086 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| 8086 Downloads |
| 8086 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 8086 Platforms |
| Wonderswan |
| MsDos |
| ARM Content |
| Learn ARM Assembly |
| Learn ARM Thumb Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World |
| Simple Samples |
| ARM Downloads |
| ARM Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| ARM Platforms |
| Gameboy Advance |
| Nintendo DS |
| Risc Os |
| Risc-V Content |
| Learn Risc-V Assembly |
| Risc-V Downloads |
| Risc-V Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| MIPS Content |
| Learn Risc-V Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World |
| Simple Samples |
| MIPS Downloads |
| MIPS Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| MIPS Platforms |
| Playstation |
| N64 |
| PDP-11 Content |
| Learn PDP-11 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Simple Samples |
| PDP-11 Downloads |
| PDP-11 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| PDP-11 Platforms |
| PDP-11 |
| UKNC |
| TMS9900 Content |
| Learn TMS9900 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World |
| TMS9900 Downloads |
| TMS9900 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| TMS9900 Platforms |
| Ti 99 |
| 6809 Content |
| Learn 6809 Assembly |
| Learn 6309 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| 6809 Downloads |
| 6809/6309 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 6809 Platforms |
| Dragon 32/Tandy Coco |
| Fujitsu FM7 |
| TRS-80 Coco 3 |
| Vectrex |
| 65816 Content |
| Learn 65816 Assembly |
| Hello World |
| Simple Samples |
| 65816 Downloads |
| 65816 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 65816 Platforms |
| SNES |
| eZ80 Content |
| Learn eZ80 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| eZ80 Downloads |
| eZ80 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| eZ80 Platforms |
| Ti84 PCE |
| IBM370 Content |
| Learn IBM370 Assembly |
| Simple Samples |
| IBM370 Downloads |
| IBM370 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| Super-H Content |
| Learn SH2 Assembly |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| SH2 Downloads |
| SH2 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| SH2 Platforms |
| 32x |
| Saturn |
| PowerPC Content |
| Learn PowerPC Assembly |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| PowerPC Downloads |
| PowerPC Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| PowerPC Platforms |
| Gamecube |
| Work in Progress |
| ChibiAndroids |
| Misc bits |
| Ruby programming |
Buy my Assembly programming book
on Amazon in Print or Kindle!



Available worldwide!
Search 'ChibiAkumas' on
your local Amazon website!
Click here for more info!


Buy my Assembly programming book
on Amazon in Print or Kindle!



Available worldwide!
Search 'ChibiAkumas' on
your local Amazon website!
Click here for more info!


Buy my Assembly programming book
on Amazon in Print or Kindle!



Available worldwide!
Search 'ChibiAkumas' on
your local Amazon website!
Click here for more info!




