68000 Assembly Programming for the Sega Genesis (Mega Drive)
Specs:
|
|
ChibiAkumas Tutorials
Lesson P5 - Bitmap Functions on the Genesis
Lesson P11 - Joystick Reading on the Genesis
Lesson P16 - Palette Definitions on the Genesis
Lesson P20 - FM Sound on the Genesis via the Z80
Lesson P21 - FM Sound on the Genesis via the 68000
Lesson P27 - Hardware Sprites on the Genesis / Megadrive
Z80 Lesson P22 - Sound with the SN76489 on the Master System, GameGear, Megadrive (Genesis) and BBC Micro!
Genesis_Technical_Overview_v1.00_1991_Sega_US PDF
MegaDrive Development Wiki
PlutieDev - Genesis Documentation and Tutorials
68000 Memory Map
|
Z80 Memory Map
There are no Ports (accessible with Z80 OUT/IN) We have to access the sound chip and 68000 cpu from these memory mapped addresses. |
VDP Registers
| RegNum | Meaning | Sample | Result | ||
| 0 | mode register 1 | ---H-1M- | $04 | no H interrupt | |
| 1 | mode register 2 | -D-V-D-P1-- | $14 | blanked, no V interrupt, DMA enable | |
| 2 | name table base for scroll A (A=top 3 bits) | --AAA--- | $30 | $C000 | |
| 3 | name table base for window (A=top 4 bits / 5 in H40 Mode) | --AAAAA- | $3C | $F000 | |
| 4 | name table base for scroll B (A=top 3 bits) | -----AAA | $07 | $E000 | |
| 5 | sprite attribute table base (A=top 7 bits / 6 in H40) | -AAAAAAA | $6C | $D800 | |
| 6 | unused register | $00 | $00 | ||
| 7 | background color (P=Palette C=Color) | --PPCCCC | $00 | $00 | |
| 8 | unused register | $00 | $00 | ||
| 9 | unused register | $00 | $00 | ||
| 10 | H interrupt register (L=Number of lines) | LLLLLLLL | $FF | $FF (esentially off) | |
| 11 | mode register 3 | ----IVHL | $00 | disable ext int, full H/V scroll | |
| 12 | mode register 4 (C bits both1 = H40 Cell) | C---SIIC | $81 | 40 cell horizontal mode, no interlace | |
| 13 | H scroll table base (A=Top 6 bits) | --AAAAAA | $37 | $FC00 | |
| 14 | unused register | $00 | $00 | ||
| 15 | auto increment (After each Read/Write) | NNNNNNNN | $01 | $01 | |
| 16 | scroll size (Horiz & Vert size of ScrollA & B) | --VV-HH | $01 | V 32 cell, H 64 cell | |
| 17 | window H position (D=Direction C=Cells) | D�CCCCC | $00 | $00 | |
| 18 | window V position (D=Direction C=Cells) | D�CCCCC | $00 | $00 | |
| 19 | DMA length count low | LLLLLLLL | $FF | $00FF | |
| 20 | DMA length count high | HHHHHHHH | $FF | $Ffxx | |
| 21 | DMA source address low | LLLLLLLL | $00 | $xxxx00 | |
| 22 | DMA source address mid | MMMMMMMM | $00 | $xx00xx | |
| 23 | DMA source address high (C=CMD) | CCHHHHHH | $80 | VRAM fill, addr $00xxxx |
Color Ram addresses
| Palette | ColorNum | Address | Palette | ColorNum | Address | Palette | ColorNum | Address | Palette | ColorNum | Address |
| Palette 0 | Color 0 | $C0000000 | Palette 1 | Color 0 | $C0200000 | Palette 2 | Color 0 | $C0400000 | Palette 3 | Color 0 | $C0600000 |
| Color 1 | $C0020000 | Color 1 | $C0220000 | Color 1 | $C0420000 | Color 1 | $C0620000 | ||||
| Color 2 | $C0040000 | Color 2 | $C0240000 | Color 2 | $C0440000 | Color 2 | $C0640000 | ||||
| Color 3 | $C0060000 | Color 3 | $C0260000 | Color 3 | $C0460000 | Color 3 | $C0660000 | ||||
| Color 4 | $C0080000 | Color 4 | $C0280000 | Color 4 | $C0480000 | Color 4 | $C0680000 | ||||
| Color 5 | $C00A0000 | Color 5 | $C02A0000 | Color 5 | $C04A0000 | Color 5 | $C06A0000 | ||||
| Color 6 | $C00C0000 | Color 6 | $C02C0000 | Color 6 | $C04C0000 | Color 6 | $C06C0000 | ||||
| Color 7 | $C00E0000 | Color 7 | $C02E0000 | Color 7 | $C04E0000 | Color 7 | $C06E0000 | ||||
| Color 8 | $C0100000 | Color 8 | $C0300000 | Color 8 | $C0500000 | Color 8 | $C0700000 | ||||
| Color 9 | $C0120000 | Color 9 | $C0320000 | Color 9 | $C0520000 | Color 9 | $C0720000 | ||||
| Color 10 | $C0140000 | Color 10 | $C0340000 | Color 10 | $C0540000 | Color 10 | $C0740000 | ||||
| Color 11 | $C0160000 | Color 11 | $C0360000 | Color 11 | $C0560000 | Color 11 | $C0760000 | ||||
| Color 12 | $C0180000 | Color 12 | $C0380000 | Color 12 | $C0580000 | Color 12 | $C0780000 | ||||
| Color 13 | $C01A0000 | Color 13 | $C03A0000 | Color 13 | $C05A0000 | Color 13 | $C07A0000 | ||||
| Color 14 | $C01C0000 | Color 14 | $C03C0000 | Color 14 | $C05C0000 | Color 14 | $C07C0000 | ||||
| Color 15 | $C01E0000 | Color 15 | $C03E0000 | Color 15 | $C05E0000 | Color 15 | $C07E0000 |
Colors are defined by 16 bits in the following format
| F | E | D | C | B | A | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| - | - | - | - | B2 | B1 | B0 | - | G2 | G1 | G0 | - | R2 | R1 | R0 | - |
Tilemaps... Scroll-A,Scroll-B and Window
There are 3 Tilemaps on the Genesis... Scroll-A and Scroll-B are 2 scrolling layers of tilemap...
There is a 3rd known as the 'Window' which cannot scroll - it's intended as a HUD and replaces Scroll-A. a 'Fixed point' is defined on the screen, and everything above or below, and to the Left or Right of that point is the window (meaning it cannot be in the centre). Depending on the tile priority Window can be in front of, or behind Scroll-B
The VRAM address of these is defined by various registers, here are the suggested defaults.
| Tilemap | Reg Setting | Vram Address |
| Scroll-A | R2=$30 | $C000 |
| Scroll-B | R4=$07 | $E000 |
| Window | R3=$3C | $F000 |
Scrolling!
Scrolling on the Genesis is odd!
Normally we would scroll the whole tilemap horizontally and vertically by a number of pixels... but we can actually do more!
If we wish,We can scroll individual 'Strips' of the tilemap by different amounts!...
We can scroll the Vertical strips in 'chunks' of 16 pixels (Two tiles)
We can scroll the horizontal strips in 'chunks' of 8 pixels (one tile) OR even one line!
These are defined by reg R11... a setting of $00 scrolls the whole
tilemap in one unit. $06 scrolls in blocks, $07 scrolls horizontally in
lines (vertically always scrolls in 'Chunks'
Vertical scrolling is defined by something called 'VSRAM' it's defined like the palette with special addresses. where as colors use the $C000 range, VSRAM use the $A000 range.
| Scroll-A Horizontal |
Scroll-B Horizontal | Scroll-A Vertical | Scroll-B Vertical |
|
| VRAM Address* (Word) |
$DC00-$DFFC | $DC02-$DFFE | ||
| VSRAM address* (Word) |
$000-$04C | $002-$04E |
*To select a VSRAM address put the desired address in #$4xxx0010 and write
to VDP_Ctrl port
*The VRAM address used for Hscroll is defined by R13... if R13=$37 then the base will be $DC00
Vram Addressing
| The Genesis has 64k Vram - the
purpose of each memory position is configurable, but a suggested
memory map is shown to the right. Selecting a memory address is performed by sending 4 bytes... to the Control port, however the structiure of these bytes - and their relation to the address selected is slightly odd.. this is possibly due the "Backwards compatibility" with the SMS Genesis tiles are 8x8, and 4 bits per pixel, so 32 bytes per tile |
|
|
Genesis Joystick Ports
Each joystick has two ports - one for Reading/Writing Data, and one
Control port. To set the direction (Read or Write) of each bit of the data
port (0=Read, 1=Write)
We will need to set bit 6 to Write to read all the Genesis Buttons
| End address | Description |
| $A10003 | Controller 1 data |
| $A10005 | Controller 2 data |
| $A10009 | Controller 1 control |
| $A1000B | Controller 2 control |
The Genesis Joystick ports are backwards compatible with the Master system, therefore we have to send a sequence of 1's and 0's to the 'TH' bit (Bit 6) to select the different buttons available
Note: Some of the buttons are duplicated in multiple read configurations.
| TH Bit Write | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | (TH) | C | B | Right | Left | Down | Up |
| 0 | 0 | (TH) | Start | A | 0 | 0 | Down | Up |
| 1,0,1,0,1*,0 | 0 | (TH) | C | B | X | Y | Z | Mode |
* We should perform a write of 0 to TH afterwards to reset sequence (1,0,1,0,1,0)
Sound
The Genesis has backwards compatibility with the SMS/GG SN76489If we're getting the Genesis Z80 to control the SN76489, we can just send data to port &7F again!
Unlike the NeoGeo, we can access the sound chip from the 68000 - which is probably easier!... we do this by writing to port &C00011
The data uses the format below
| Bits | |||||||||
| Command | Bit Details | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Format Template | L=Latch C=Channel T=Type XXXX=Data | L | C | C | T | D | D | D | D |
| Tone - Command 1/2 | C=Channel L=tone Low data | 1 | C | C | 0 | L | L | L | L |
| Tone - Command 2/2 | H= High tone data (Higher numbers = lower tone) | 0 | - | H | H | H | H | H | H |
| Volume | C=Channel (0-2) V=Volume (15=silent 0=max) | 1 | C | C | 1 | V | V | V | V |
| Noise Channel | (Channel 3) M=Noise mode (1=white) R=Rate (3=use tone 2) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | - | M | R | R |
Tilemap
Tilemap A is defined by addresses &C000 onwards - each tile is defined by 2 bytes
The tilemap is 64 tiles wide and 32 tiles tall
| F | E | D | C | B | A | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
| L | P | P | V | H | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T=Tille number H=Hflip V=vflip P=palette number L=Layer (in front of /behind sprites) |
Tile pattern data is NOT in bitplane format, it's in the same format as 16 color systems like the MSX2 or SAM coupe. Two pixels color information is held in a single byte, so one 32 bit long defines all 8 pixels of a tile
Sprites In H40 mode (the mode used in these tutorials), we can have
up to 80 sprites onscreen... (H32 mode can do only 64)
Each sprite can be 8x8 to 32x32
The position (and other settings) are defined by 8 by (4 Words) per
sprite.
The first visible pixel is at sprite (X,Y) pos (128,128)
| Address | Sprite Num | Details |
| $D800 | 1 | Ypos |
| $D802 | 1 | Size,Link |
| $D804 | 1 | Palette,Flip,Pattern |
| $D806 | 1 | Xpos |
| $D808 | 2 | Ypos |
| $D80A | 2 | Size,Link |
| $D80C | 2 | Palette,Flip,Pattern |
| $D80E | 2 | Xpos |
| $D810 | 3 | Ypos |
| � | ||
| $D9FF | 64 | Xpos � Last Sprite of H32 |
| � | ||
| $DA7F | 80 | Xpos � Last Sprite of H80 |
As we can see, Each sprite has 4 words, they use the same pattern data as the background...
| Address | F | E | D | C | B | A | 9 | 8 | |
7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | Details |
| $D800 | - | - | - | - | - | - | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y-Pos | |
| $D802 | - | - | - | - | W | W | H | H | - | L | L | L | L | L | L | L | Width (8,16,24,32), Height (8,16,24,32), Link (to next sprite) | |
| $D804 | P | C | C | V | H | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Priority, Color palette , Vflip, Hflip, tile Number | |
| $D806 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X-pos |
The 'Link' Connects the sprites together, each sprite should point to the next (starting from Sprite 0) and the last sprite should point back to sprite 0, this is not like neogeo chaining,it doesn't make the sprites move together it doesn't make the sprites move together - it defines the 'draw order' of the active sprites.
Multi pattern Sprites
A basic sprite is 8x8, but sprites can be enlarged up to 32x32... however
this sprite will still be made up of 8x8 pattern data...
If we want a larger sprite, we need to break up the sprite into 8x8 blocks, and save those in VRAM in the correct order - the tiles go down first, and across second, as shown below:
| 1 | 5 | 9 | 13 |
| 2 | 6 | 10 | 14 |
| 3 | 7 | 11 | 15 |
| 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
Mouse Reading
The Genesis mouse can be read from the standard joystick ports.
We need to write #%01100000 to $A10009 for Joy Port 1, or $A1000B for Joy
Port 2
We then send and receive bytes from port $A10003 for Joy Port 1, or
$A10005 for Joy Port 2
Here is the sequence of bytes we send, and bits we receive back:
| Sent Byte | Received Bits | ||||||||
| 7
|
6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
0 |
||
| $60 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| $20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| $00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| $20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| $00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Y
Overflow |
X
Overflow |
Y Sign | X Sign | Overflow flag / Move direction |
| $20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Start | Middle | Left | Right | Buttons |
| $00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | X axis High byte | X | |||
| $20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | X axis Low byte | X | |||
| $00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Y axis High byte | Y | |||
| $20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Y axis Low byte | Y | |||
| $60 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | Transfer Stop |
Sound on the Genesis via SN76489
The Genesis still supports the Master System & Gamegear sound chip, and we can use it in the same way as those systems if we wish... the data we send is in the format below| Bits | |||||||||
| Command | Bit Details | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Format Template | L=Latch C=Channel T=Type XXXX=Data | L | C | C | T | D | D | D | D |
| Tone - Command 1/2 | C=Channel L=tone Low data | 1 | C | C | 0 | L | L | L | L |
| Tone - Command 2/2 | H= High tone data (Higher numbers = lower tone) | 0 | - | H | H | H | H | H | H |
| Volume | C=Channel (0-2) V=Volume (15=silent 0=max) | 1 | C | C | 1 | V | V | V | V |
| Noise Channel | (Channel 3) M=Noise mode (1=white) R=Rate (3=use tone 2) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | - | M | R | R |
We looked at using the SN76489 on the Genesis in the Z80 Tutorials here!
FM Sound on the Genesis via YM2612
| The Genesis uses 2 pairs of Address and Data ports to access ALL
the sound registers - these can be accessed by the Z80, or 68000,
but we must disable the Z80 if we want to use the 68000, We can do this with the commands shown the right Learn more about the registers with the YM2608 manual (Japanese Original) Note... The YM2612 only has the FM part, and does not have the SSG of the 2608 |
move.w
#$100,$a11100 ;Z80 Bus REQ move.w #$100,$a11200 ;Z80 Reset |
|
Reg |
Purpose | A0/D0 $4000/1 $A04000/1 |
A1/D1 $4002/3 $A04002/3 |
Bits | Details |
| $22 | LFO | ALL | - | ----EFFF | E=enable F=frequency |
| $24 | Timer A low | ALL | - | TTTTTTTT | Timer bits 10-2 |
| $25 | Timer A high | ALL | - | ------TT | Timer bits 1-0 |
| $26 | Timer B | ALL | - | TTTTTTTT | Timer B |
| $27 | Ch3 CSM Mode & Ch3 Multi-Mode & Enable Timers | ALL | - | 33RROOSS | 3= Chn 3 mode / R=timer resets / O= Timer overflows / S = Timer StartStop |
| $28 | Individual Operator Key On/Off | ALL | - | OOOO-CCC | O=operator (%4321----) / C=Channel (%000=chn 1 %110=chn6) |
| $29 | SCH, IRQ Enable | ALL | - | S--IIIII | S=Sixchannel / I=IRQ Enable |
| $2A | DAC Write | ALL | - | DDDDDDDD | D=Data |
| $2B | DAC Enable | ALL | - | E------- | E=enable |
| $30 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $31 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $32 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $34 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $35 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $36 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $38 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $39 | Multiplier & Detune | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $3A | Multiplier & Detune | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $3C | Multiplier & Detune | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $3D | Multiplier & Detune | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $3E | Multiplier & Detune | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | -DDDMMMM | D=Detune / M=Multiplier |
| $40 | Total Level | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $41 | Total Level | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $42 | Total Level | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $44 | Total Level | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $45 | Total Level | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $46 | Total Level | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $48 | Total Level | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $49 | Total Level | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $4A | Total Level | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $4C | Total Level | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $4D | Total Level | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
| $4E | Total Level | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | -TTTTTTT | T=Total Level (0=largest) |
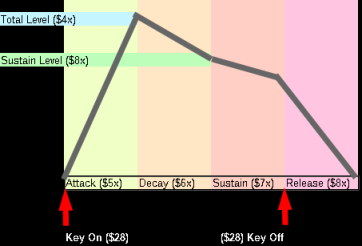
| $50 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $51 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $52 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $54 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $55 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $56 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $58 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $59 | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $5A | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $5C | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $5D | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $5E | Attack Rate & Rate Key Scaling | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | RR-AAAAA | R=Rate Scaling / A = Attack rate |
| $60 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $61 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $62 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $64 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $65 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $66 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $68 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $69 | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $6A | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $6C | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $6D | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $6E | Decay Rate & AM Enable | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | A--DDDDD | A=Amplitude Mod Enable / D= Decay rate |
| $70 | Sustain Rate | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $71 | Sustain Rate | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $72 | Sustain Rate | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $74 | Sustain Rate | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $75 | Sustain Rate | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $76 | Sustain Rate | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $78 | Sustain Rate | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $79 | Sustain Rate | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $7A | Sustain Rate | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $7C | Sustain Rate | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $7D | Sustain Rate | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $7E | Sustain Rate | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | ---SSSSS | S=Sustain Rate |
| $80 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $81 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $82 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $84 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $85 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $86 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $88 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $89 | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $8A | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $8C | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $8D | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $8E | Release Rate & Sustain Level | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | SSSSRRRR | S=Sustain Level / Release Rate |
| $90 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch1 Op1 | Ch4 Op1 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $91 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch2 Op1 | Ch5 Op1 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $92 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch3 Op1 | Ch6 Op1 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $94 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch1 Op2 | Ch4 Op2 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $95 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch2 Op2 | Ch5 Op2 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $96 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch3 Op2 | Ch6 Op2 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $98 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch1 Op3 | Ch4 Op3 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $99 | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch2 Op3 | Ch5 Op3 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $9A | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch3 Op3 | Ch6 Op3 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $9C | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch1 Op4 | Ch4 Op4 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $9D | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch2 Op4 | Ch5 Op4 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $9E | SSG-Envelope Generator | Ch3 Op4 | Ch6 Op4 | ----EEEE | E=Envelope Gen |
| $A0 | Frequency low (Write Second) | Ch1 | Ch4 | PPPPPPPP | P=Frequency Position L |
| $A1 | Frequency low (Write Second) | Ch2 | Ch5 | PPPPPPPP | P=Frequency Position L |
| $A2 | Frequency low (Write Second) | Ch3 | Ch6 | PPPPPPPP | P=Frequency Position L |
| $A4 | Frequency high & Octave (Write first) | Ch1 | Ch4 | --OOOPPP | O=Octive / P=Position H |
| $A5 | Frequency high & Octave (Write first) | Ch2 | Ch5 | --OOOPPP | O=Octive / P=Position H |
| $A6 | Frequency high & Octave (Write first) | Ch3 | Ch6 | --OOOPPP | O=Octive / P=Position H |
| $A8 | Frequency low during Multi-Mode | Ch3 Op2 | - | PPPPPPPP | P=Frequency Position L |
| $A9 | Frequency low during Multi-Mode | Ch3 Op3 | - | PPPPPPPP | P=Frequency Position L |
| $AA | Frequency low during Multi-Mode | Ch3 Op4 | - | PPPPPPPP | P=Frequency Position L |
| $AC | Frequency high & Octave during Multi-Mode | Ch3 Op2 | - | --OOOPPP | O=Octive / P=Position H |
| $AD | Frequency high & Octave during Multi-Mode | Ch3 Op3 | - | --OOOPPP | O=Octive / P=Position H |
| $AE | Frequency high & Octave during Multi-Mode | Ch3 Op4 | - | --OOOPPP | O=Octive / P=Position H |
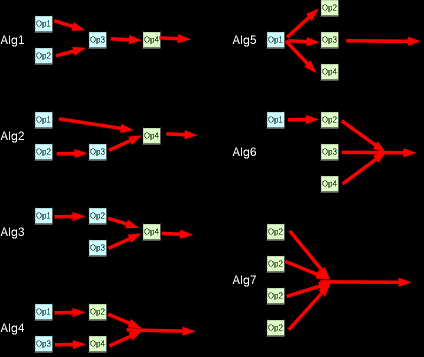
| $B0 | Algorithm & Feedback | Ch1 | Ch4 | --FFFAAA | F=Feedback / A=Algorithm |
| $B1 | Algorithm & Feedback | Ch2 | Ch5 | --FFFAAA | F=Feedback / A=Algorithm |
| $B2 | Algorithm & Feedback | Ch3 | Ch6 | --FFFAAA | F=Feedback / A=Algorithm |
| $B4 | FMS & AMS & Stereo | Ch1 | Ch4 | LRAA-FFF | Left / Right (1=on) / A=Amplitude Mod Sensitivity / F=Frequency Mod Sensitivity |
| $B5 | FMS & AMS & Stereo | Ch2 | Ch5 | LRAA-FFF | Left / Right (1=on) / A=Amplitude Mod Sensitivity / F=Frequency Mod Sensitivity |
| $B6 | FMS & AMS & Stereo | Ch3 | Ch6 | LRAA-FFF | Left / Right (1=on) / A=Amplitude Mod Sensitivity / F=Frequency Mod Sensitivity |
| View Options |
| Default Dark |
| Simple (Hide this menu) |
| Print Mode (white background) |
| Top Menu |
| ***Main Menu*** |
| Youtube channel |
| Patreon |
| Introduction to Assembly (Basics for absolute beginners) |
| Amazon Affiliate Link |
| AkuSprite Editor |
| ChibiTracker |
| Dec/Bin/Hex/Oct/Ascii Table |
| Alt Tech |
| Archive.org |
| Bitchute |
| Odysee |
| Rumble |
| DailyMotion |
| Please note: I wlll upload more content to these alt platforms based on the views they bring in |
| 68000 Content |
| ***68000 Tutorial List*** |
| Learn 68000 Assembly |
| Hello World Series |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Simple Samples |
| Grime 68000 |
| 68000 Downloads |
| 68000 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 68000 Platforms |
| Amiga 500 |
| Atari ST |
| Neo Geo |
| Sega Genesis / Mega Drive |
| Sinclair QL |
| X68000 (Sharp x68k) |
| 8086 Content |
| Learn 8086 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| 8086 Downloads |
| 8086 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 8086 Platforms |
| Wonderswan |
| MsDos |
| ARM Content |
| Learn ARM Assembly |
| Learn ARM Thumb Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World |
| Simple Samples |
| ARM Downloads |
| ARM Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| ARM Platforms |
| Gameboy Advance |
| Nintendo DS |
| Risc Os |
| Risc-V Content |
| Learn Risc-V Assembly |
| Risc-V Downloads |
| Risc-V Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| MIPS Content |
| Learn Risc-V Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World |
| Simple Samples |
| MIPS Downloads |
| MIPS Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| MIPS Platforms |
| Playstation |
| N64 |
| PDP-11 Content |
| Learn PDP-11 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Simple Samples |
| PDP-11 Downloads |
| PDP-11 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| PDP-11 Platforms |
| PDP-11 |
| UKNC |
| TMS9900 Content |
| Learn TMS9900 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World |
| TMS9900 Downloads |
| TMS9900 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| TMS9900 Platforms |
| Ti 99 |
| 6809 Content |
| Learn 6809 Assembly |
| Learn 6309 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| 6809 Downloads |
| 6809/6309 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 6809 Platforms |
| Dragon 32/Tandy Coco |
| Fujitsu FM7 |
| TRS-80 Coco 3 |
| Vectrex |
| 65816 Content |
| Learn 65816 Assembly |
| Hello World |
| Simple Samples |
| 65816 Downloads |
| 65816 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| 65816 Platforms |
| SNES |
| eZ80 Content |
| Learn eZ80 Assembly |
| Platform Specific Series |
| eZ80 Downloads |
| eZ80 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| eZ80 Platforms |
| Ti84 PCE |
| IBM370 Content |
| Learn IBM370 Assembly |
| Simple Samples |
| IBM370 Downloads |
| IBM370 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| Super-H Content |
| Learn SH2 Assembly |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| SH2 Downloads |
| SH2 Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| SH2 Platforms |
| 32x |
| Saturn |
| PowerPC Content |
| Learn PowerPC Assembly |
| Hello World Series |
| Simple Samples |
| PowerPC Downloads |
| PowerPC Cheatsheet |
| Sources.7z |
| DevTools kit |
| PowerPC Platforms |
| Gamecube |
| Work in Progress |
| ChibiAndroids |
| Misc bits |
| Ruby programming |
Buy my Assembly programming book
on Amazon in Print or Kindle!



Available worldwide!
Search 'ChibiAkumas' on
your local Amazon website!
Click here for more info!


Buy my Assembly programming book
on Amazon in Print or Kindle!



Available worldwide!
Search 'ChibiAkumas' on
your local Amazon website!
Click here for more info!


Buy my Assembly programming book
on Amazon in Print or Kindle!



Available worldwide!
Search 'ChibiAkumas' on
your local Amazon website!
Click here for more info!